I WANT
RELATED LINKS
I WANT
RELATED LINKS
RELATES LINKS
I WANT
RELATES LINKS
Services
Related Links

คำค้นหาที่แนะนำ
ผลการค้นหา "{{keyword}}" ไม่ปรากฎแต่อย่างใด
ข้อแนะนำในการค้นหา
- ตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของข้อความ
- ตรวจสอบภาษาที่ใช้ในการพิมพ์
- เปลี่ยนคำใหม่ กรณีไม่พบผลการค้นหา
Use and Management of Cookies
We use cookies and other similar technologies on our website to enhance your browsing experience. For more information, please visit our Cookies Notice.
- Personal Banking
- Stories & Tips
- Protect My Family
- Cervical cancer, the cancer that kill Thai woman the most
- Personal Banking
- ...
- Cervical cancer, the cancer that kill Thai woman the most
Cervical cancer, the cancer that kill Thai woman the most
03-08-2020
Life is difficult as a woman. Not only have they get pregnant and need to bear a baby for 9 months, but the genitals or other organs that are used for taking care of babies such as the cervix, ovary, and breasts, are quite at risk to have cancer, a deadly disease killing many human beings. Many of you might have known that cancer which mostly found in women is breast cancer. However, cancer that is the first most common cause of death for Thai women is “cervical cancer”. There are about 53,000 women patients who are suffered from this cancer around the world, 85% of them are from developing countries, like Thailand. Today, we will learn more about the cause of cervical cancer, how to do a basic observation, treatment, chance of recovery, and, importantly, how to prevent yourself from cervical cancer.
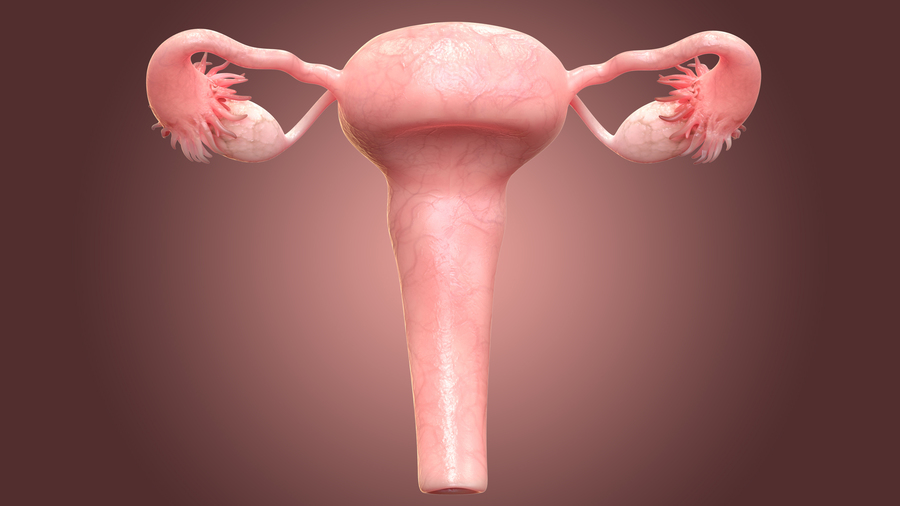
What is a cervix and where is it located?
A cervix is a 2 centimeters length part of the uterus locating in the vagina. A cervix can be divided into 2 parts—1. Ectocervix, external part, a smooth white-pink squamous skin with flat cells, and 2. Endocervix, a pink-red skin with a hole in the middle covered with columnar cells that can eject the mucous. The area connecting to the Ectocervix and Endocervix is called Transition Zone, a common area for cervical cancer to occur.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
The causes of the cervical cancer can be either from the chemical causing a chronic irritation or factors that affect the cells. But the main factor that causes cervical cancer is the Human Papilloma Virus, or HPV. This disease can be transmitted by physical contact, mainly from sex activity. When the patient has contacted with HPV, it will take about 10-15 years for the disease to develop, and the symptom will clearly show at the age of 30-60 years. This disease can be eliminated by body system but some that cannot be eliminated can change into the dreadful cancer. The other factors that can cause cervical cancer are:
- Age, cervical cancer mostly found in women older than 40 years old.
- Early sexual activity in individuals who are younger than 18 years old.
- Many sexual partners, the greater chance of acquiring HPV.
- Smoking
- Deliver baby more than 3 times.
- An immunodeficiency such as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
- A person who never had an internal examination checking for precancerous conditions. In this stage, a symptom mostly does not show but can be found by cytological examination called Pep Smear. Early detection can give a greater chance for cure and prevention.
Cervical cancer: Symptoms
In the early stage, cancer gives most people no symptom that exclusively indicates the disease. However, when the disease becomes more severe, the symptoms may occur as follows:
- Vagina bleeding, either light bleeding after intercourse or blood spots between the periods.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Menstrual bleeding that is longer and more than usual.
- Anorexia, weight loss.
- Watery, thick, bloody vaginal discharge that may have a foul odor or odorless.
- Blood in the stool, urine (in case that cancer spreads to the urinary bladder or sigmoid colon),
- Bleeding after menopause,
- Unexplained, persistent pelvic and/or back pain,
- In case of the severe stage, patients could feel a cramp in their lower abdomen, encounter difficulty in urinating and excretion, or kidney dysfunction that could be fatal
- Leg swollen as cancer has spread to the Lymph gland.
If these symptoms were found, you should see the obstetrician as soon as possible as these are the signs of cervical cancer.
How to check whether you have cervical cancer?
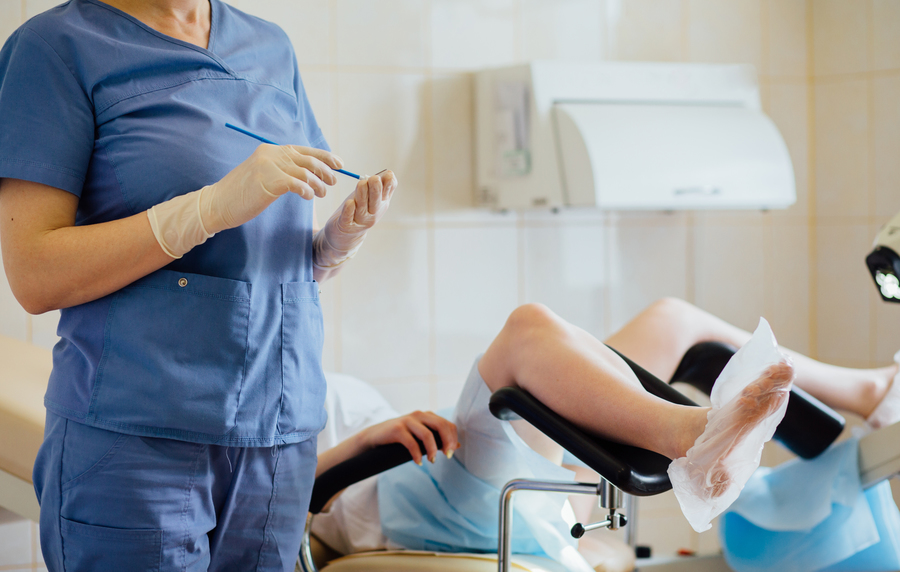
There are many examinations to check for cervical cancer.
Pap smear –involves collecting cells from the cervix and inside vagina then spread on the glass slide and dye with the special methodology before letting the pathologist or expert examine the unusual cell from the microscope. This is the most popular method used.
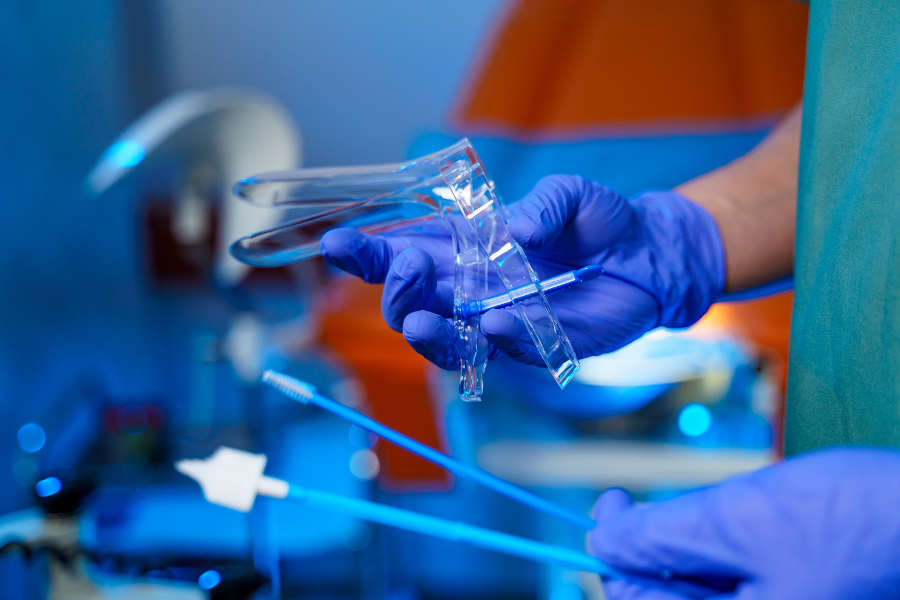
colposcope This is a tool used to find the abnormal cells that can become cancerous for a better examination result.
Liquidbased Cytology –This methodology is done in the lab. The special tools are used for collecting the cell from the cervix, similar to Pap Smear methodology. After that, the cell will be kept in the chemical liquid and send to an automatic machine for examination.
HPV-DNA –This is the direct methodology for finding HPV. This method can provide rapid and accurate results but it is still expensive.
Who should get a cervical cancer examination?
Women who have sexual intercourse should have this examination at least once a year. For those who have not had sexual intercourse, at the age of 35, the examination should be done after a period, or 1 week before the following period. Avoid sexual intercourse, vaginal suppositories, or douche for 2 weeks before having an examination. For the menopause or those who have the contraceptive injection, without the period, the examination can be done any time.

Cervical cancer levels
There are 4 levels as follows:
- Level 0: The cancer is still on the upper part of the cervix,
- Level 1: The cancer is at the cervix and begins spreading,
- Level 2: Cancer has spread from the cervix lining into the deeper tissue but not more than 1/3 of the vaginal area,
- Level 3: The tumor involves the lower third of the vagina, and/or has spread to the pelvic wall, and/or causes swelling of the kidney, called hydronephrosis, or stops a kidney from functioning, causing urinary retention,
- Level 4: Cancer has spread from the sexual organ/pelvic to the intestine, urinary bladder, or other parts of the body.
Cervical cancer treatment
Cervical cancer can be completely treated if it has been found early. The treatment of this cancer depends on the cancer levels as mentioned. For the precancerous lesion, the doctor might suggest the patient to have the surgery as it is the best method to provide the best result. For the medium level, radiation and chemotherapy will be used, and the result will be quite impressive. For the final level, mostly, palliative treatment and pain reduction will be used.
The effect is depended on the treatment. Normally, to have the surgery, there will be side effects, for example, heavy bleeding or an infected wound after the operation. For the radiation, mostly, the side effects will occur about 2-3 years after the treatment. The side effect, for example, bloody urine and stool. For chemotherapy, the normal side effects occurred are having nausea and vomiting, fatigue, having Leukopenia causing an easy infection, or having the hair fall affected by some drugs. By the way, the side effects will be notified by the doctor before having the treatment.
How to protect yourself from the cervical cancer
The best way is to do the cervical cancer examination regularly, stop smoking, do not have many sexual partners, exercise, and consume healthy food to strengthen the immunity, along with having the vaccine since it can protect you from HPV infection, 16 and 18, for about 90-100 percent, in non-infected patients. The effect will occur within 1 month after the third vaccination. For the best effect, the vaccination should be done, for the woman with the age of 9-26, before having HPV infection, before having the first sexual intercourse.
Cancer is near us since it has killed about 13% of the world’s population. Thus, we must take care of ourselves regularly and have an annual health examination before the spread of any disease. But the certain is uncertainty. Although we have taken care of ourselves the best we can, there is a chance to get cancer or another sickness. So, having insurance will be one of the methods to help you with the medical bills that cancer caused, which requires a high payment with a long-time recovery. From this, some might have lost their income. SCB Multi Care Multi Claim is one of the best choices for those who want health insurance but do not want to waste the money since the premium will be returned to you if you do not have any serious sickness. For more information, go to https://www.scb.co.th/th/personal-banking/insurance/cancer-insurance.html
Reference